Defining nutrition science means exploring the relationship between a vast amount of nutrients and how they impact growth, health, maintenance, and disease when interacting with a human being or any other living organism.
The study of nutrition can be traced back to the 6th century BC. Nutrition science definition as we know it begins in the early 20th century, which brought about the scientific study of calories as units of expended energy. The field of Nutrition Science continues to evolve. Recent developments in the 21st-century research regarding the relationship between one’s dietetic habits and one’s health have made nutrition an important, relevant aspect of living healthy.
Related:
- Best Nutritional Science Degree Programs
- Best Online Nutritional Science Degree Programs
- Most Affordable Nutritional Science Degree Programs
- Best Online Nutritional Science Certificate Programs
Given the above-noted refined nutrition science definition, more and more students are becoming interested in the nutrition field for career opportunities. Nutrition specialists help people take charge of their well-being, or to become a part of the food preparation portion of the nutrition field. There are many reasons to become a dietitian, but students often have questions regarding the education required to become a Registered Dietician or a Nutritionist:
- How long does it take to become a dietitian?
- Is becoming a registered dietitian worth it?
- Can a student earn their nutritional sciences degree online?
All of these questions will be answered to line up the reasons to become a dietitian. First, though, let’s review how being a dietitian, pros and cons, add up.
The Pros:
The nutrition field expands routinely as astounding technological techniques reveal new, relevant developments. As a result, career opportunities and nutrition specialties amount to rewarding careers. A nutrition degree graduate has a variety of skills that impact many lives in endless ways. A Registered Dietitian may work independently or in clinical settings advising clients as to how their nutritional intake can boost their health.
The Cons:
How long does it take to become a dietitian? It can take quite a while, depending on what kind of degree you choose. A nutrition degree, by itself, may limit career advancement, as knowledge gained from the degree is comprehensive but somewhat limited. Professional Registered Dietitians have found that combining a nutrition degree with another related degree is the key to the door of career possibilities and growth. Potential degrees that enhance a nutrition degree include chemistry, counseling, and even business.
When it comes to being a dietitian, pros and cons are pretty clear; if you’re interested in food and believe in helping people improve their health, the pros far outweigh the cons. Still asking yourself:
- How long does it take to become a dietitian?
- Is becoming a registered dietitian worth it?
Read on to discover the reasons to become a dietitian. If it is to influence and motivate people to reach for a healthy version of themselves, then a Registered Dietitian career might be the perfect fit.
Nutrition and Dietetics Education: School/Program Accreditation
Choosing to earn a college degree by enrolling in nutrition science courses can be a life-impacting decision. How does one know if the school they choose will provide an education that is worth the cost of tuition?
The purpose of a university and program accreditation can be likened to a company’s quality assurance division. Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics accreditation denotes that a school and/or degree program meets national educational standards as well as elite standards. An ACEND accredited didactic program in dietetics, for instance, signifies that a dietetics program teaches everything required for the Registered Dietitian exam. The same is true of ACEND accredited online programs.
The process of accreditation for nutrition science courses seriously studies each school’s programs and curriculum to determine if the school and coursework meet pre-determined academic, faculty, competency, and credibility standards. A government or a professional organization grants accreditation to a college or university through their qualification processes.
Regional Accreditation
There are only seven United States Department of Education (USDE) Regional Accreditation Agencies in the United States. And while the USDE does not actually accredit colleges and universities, they are tasked with the responsibility of overseeing the country’s accreditation processes conducted through the seven approved agencies. As such, regional accreditation is considered the preeminent form of accreditation. A United States Department of Education regionally accredited school provides each student with a level of certainty should they need to transfer credits or want to earn a more advanced degree.
Program Accreditation
Specialized degree programs, like an undergraduate or graduate degree in nutrition science, often opt for specialized accreditation as this type of certification speaks to the program or the degree with a curriculum that exceeds even the strictest e general accreditation programs. Students who earn a degree from a specialized accredited program will find colleges and universities respect the specialized accredited nutrition degree earned.
For those seeking an ACEND accredited didactic program in dietetics, the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics (AND) provides accreditation to nutrition science-oriented programs and degrees. The Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics is a trusted source of nutrition-based college-level certificates and degree programs, including ACEND accredited online programs. Additionally, students interested in a specialized accreditation degree program may also see a certification granted by ACEND Accreditation Standards for Didactic Programs in Dietetics. The Accreditation Standards for Didactic Programs in Dietetics delineate clear educational standards that prepares students to sit for the Commission on Dietetic Registration’s (CDR) exam.
When nearing a final decision about where to earn a degree requiring nutrition science courses, make an informed decision by selecting a specialized accredited program with certification granted by the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, or, for distance learning nutrition science degrees, look for ACEND accredited online programs.
Types of Nutrition and Dietetics Degrees
Nutrition science degree programs from the best colleges for nutrition usually take four years to finish. Students studying for their nutritionist degree have the opportunity to select an area of focus that meets the requirements of one’s desired career path. Nutrition may sometimes be a Bachelor of Science or a Bachelor of Arts, but Dietitian bachelor’s programs are usually BS. The top schools for nutrition and dietetics will often have more than one specialization available, as well.
A nutritionist degree offers several degree program options for those with a passion for a didactic program in dietetics. A bachelor degree in nutrition and dietetics offered by some of the best universities for dietetics and nutrition offer students a variety of specialties for those seeking a degree as a nutrition science major. It’s important to note that, while a bachelor’s degree usually takes 4 years, many schools are now offering 5‑year programs that allow students to earn a bachelor’s and master’s in only 5 years.
Some of the basics you’ll learn in nutrition courses include:
- medical nutrition therapy
- disease prevention
- life cycle and lifespan health
- integrative health sciences
- human nutrition
- community health promotion
- nutrition counseling
Your program might also include prerequisites like microbiology and organic chemistry.
Nutrition Science Major Specialty Programs
Consider these broad specialty categories offered by some of the best colleges for nutrition.
- Food & Business Nutrition
- Food Service Administration
- Nutrition Degree in Education
- Physiology & Metabolism
- Public Health Nutrition & Policy
Earning a bachelor’s in nutrition provides a student with the option to select from many types of nutrition degrees. A nutritionist degree, a coordinated program in dietetics, and a dietitian education provide the educational backdrop, experience, and knowledge to find a degree program offered by one of the best colleges for nutrition. Dietetics degree vs nutrition degree usually depends on the focus the program takes; if it is not intended for students to earn the Registered Dietitian license, a bachelor’s in nutrition is more focused on the nutrition itself. Fundamental coursework for most types of nutrition degrees includes:
- Biochemistry
- Biology
- Chemistry
- Community Nutrition
- Diet & Disease
- Food Science
- Human Anatomy & Physiology
- Professional Issues in Nutrition
- Research Methods in Nutrition
- The Principles of Nutrition
This classwork, offered by some of the best universities for dietetics and nutrition, focuses on the varied programs noted above required to earn a degree as a nutrition science major. Those who choose from accredited programs provided by colleges offering nutrition degrees, often choose wisely. Obtaining a bachelor’s in nutrition degree is a prudent place to begin for students who wish to reach for a career as a nutrition science major researcher or educator.
Note that the above-mentioned programs are just a sampling of the available dietitian education offered by the top schools for nutrition and dietetics.
How does a didactic program differ from a coordinated program?
This is where a dietetics degree vs nutrition degree really makes a difference. While a nutrition degree is more focused just on nutrition, the dietetics degree is designed to prepare students for the CDR exam. Students graduating from a didactic program in dietetics or from a coordinated program in dietetics both earn a bachelor’s degree.
In the best universities for dietetics and nutrition, the difference between the didactic program in dietetics and the coordinated program in dietetics is that a Didactic Program requires coursework over a four-year period; that does not include a practicum or internship. Upon graduation, students complete a dietetic internship that includes supervision for a minimum of 900 hours. When the internship is complete, the bachelor’s in nutrition degree holder becomes eligible to sit for the Registration Examination for Dietitians, the national credential required to legitimately practice as a Registered Dietitian.
In a Coordinated Program in Dietetics, a student completes the coursework required over the four-year period. A student completes their supervised internship of 900 hours during the four years it takes to complete the degree program. Essentially, the coursework and internships are similar, the difference is the amount of time required to be eligible to sit for the Registration Examination for Dietitians.
Registered Dietitians can opt to attain a board-certified specialty in the areas of pediatric nutrition, sports nutrition, oncology nutrition, and geriatrics nutrition, among others. The top schools for nutrition and dietetics tailor their curriculum to the exam, making for a high pass rate.
Remember! Graduating as nutritionist does automatically license someone who has graduated with a nutritionist degree; however, if they have completed the clinical hours, graduates of a bachelor degree in nutrition and dietetics program are eligible to sit for the Registered Dietitian exam.
The Difference Between a Nutritionist and a Dietitian
A Nutritionist and a Dietitian share similar career aspirations and objectives and attend similar nutrition major colleges. Both seek to teach families and communities how to create nutrition-savvy lives that bring about healthful living. Both degree holders are trained in similar nutrition science major colleges that promote researched nutritional standards. However, their educational background and certification requirements differ.
The Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics credentials a dietitian as a Registered Dietitian. This dietitian designation requires a bachelor’s degree through an accredited program, the completion of a supervised internship and passing the Registration Examination for Dietitians.
A nutrition science major operates without the same regulations as a Dietitian. In addition, state laws differ as to the acceptable education and experience required to define oneself as a nutritionist. So while a dietitian is a national certification, a nutritionist is usually defined by state-level regulations, if at all (some states have no regulation).
The Center for Nutrition Advocacy manages a database regarding state laws. Check out their website for specific information regarding the laws in the state you wish to practice.
Online Nutrition and Dietetics Degree Programs
Aspiring professional nutritionists and dietitians must be certain of their state’s license requirements before selecting from the many nutritionist online programs. It is counterproductive selecting a bachelor’s in nutrition online degree program that does not meet licensure requirements.
Nutritionist and Dietitian education has kept pace with the explosion of online distance-learning platforms. Students who need flexible scheduling and affordable online courses can access some of the best online nutrition degree programs across the country. Additionally, students have the opportunity to select from the following partial list of programs.
- Bachelor’s in Nutrition online
- Didactic Program in Dietetics online
- Dietetics Degree online
- Online Holistic Nutrition degree
- Online Nutrition Associates degree
- Post Baccalaureate Dietetics online
- Registered Dietitian programs online
Nutritionist online programs offer students various levels of online degrees. An online nutrition associate’s degree can be completed in about 2+ years for those who want a formal introduction into the nutrition industry. Students can also choose from some of the best online nutrition certification programs. A nutrition distance learning bachelor’s degree is generally completed in four years, but accelerated degrees can cut down the time tremendously. Registered Dietitian programs online offer convenience and flexibility to students who face time limitations.
From an online holistic nutrition degree to Registered Dietitian programs online, students now have the opportunity to study for their degree through a Didactic Program in Dietetics Online from some of the best online nutrition degree programs across the country.
Online Nutrition Degree Course Requirements
Students enrolled in a bachelor’s nutritionist online program will find that they study general core education classes during their freshman and sophomore years. While each school differs slightly, the first two years’ coursework includes:
- Arts & Humanities
- Biology
- Chemistry
- Foreign Languages
- Psychology
among other general education classes. During a student’s junior and senior years, the best online nutrition degree programs require the completion of:
- Anatomy & Physiology
- Dietary Planning
- Food Science
- Nutrition Therapy
- Nutrition’s Social Aspects
among other core courses and electives.

Nutritionist and Dietitian Certifications and Licenses
A Registered Dietician and a professional with a Nutritionist Certification are required to follow state-specific educational mandates, as well as examination guidelines set forth by each state’s relevant oversight agency. Guidelines for a Registered Dietitian or a Nutritionist Dietitian vary from state to state. Students should understand the state-mandated requirements for their state before selecting a school or an online nutrition program. When a student understands their state’s requirements, it is easy to envision the commitment and time required to complete their educational objective.
As the world faces the growing epidemic of obesity (and the serious maladies obesity causes), the various facets of the medical community have a powerful renewed interest in the mechanics of healthy eating and healthy lifestyle choices. This is where a Nutritionist Dietitian or a professional with a Dietetics Certification can make a world of difference. One prominent example of a national initiative was the Let’s Move program initiated by the Obama White House.
How to Become a Registered Dietitian
The Registered Dietitian (RD) credential is earned when a nutritionist degree holder passes the national RD examination — the exam that tests their knowledge against the Commission on Dietetic Registration’s (CDR) criteria. The Registered Dietitian (RD) or the Registered Dietitian Nutritionist (RDN) licenses are designations that are awarded by the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics. According to legal experts, the RDN variation is one and the same as the RD designation. It simply communicates a more comprehensive awareness of the nutritional aspect of what a licensee can offer.
Remember that all RD’s are nutrition experts but not all nutritionists are Registered Dietitians. Those interested in a career in nutrition can opt for a Nutritionist Certification, a Dietetics Certification or nutrition careers without RD.
The Registered Dietitian Exam
The eligibility requirements for the RD national exam follow three primary pathway options. The first eligibility option refers to bachelor’s degree graduates who have completed the Dietetic Internship through a regionally accredited school, and a degree program accredited by ACEND — Accreditation Standards for Didactic Programs in Dietetics.
The second eligibility option for the Registered Dietitian examination is for those who have graduated from Coordinated Nutrition Program that is ACEND accredited, and a college or university that has been granted regional accreditation.
The third eligibility option is open to Didactic Program in Dietetics graduates from a regionally accredited school, and an ACEND accredited program.
Additional RD examination options are available for Doctorate Degree graduates, Reciprocity of Eligibility, the Canadian RD, and International Dietetics graduates.
Careers in Nutrition Sciences
Is nutrition and dietetics a good career move? Careers in nutrition are plentiful, and the job market is expanding far faster than the average (15% by BLS stats). Bachelor’s in Nutrition jobs are available in a variety of clinical and non-clinical environments. Careers in nutrition, careers in nutrition and wellness, careers in nutrition and food science, or careers in nutrition and health offer graduates various career options, capacities, and settings that include:
- Government agencies
- Hospitals
- Nursing homes
- Schools
These careers in nutrition require professionals to set meal plans in accordance with nutrition guidelines and to track the progress of clients over time. Additionally, nutritional science jobs can be found in clinics, gyms, or counseling programs. For those who want to work independently, consider the following careers in nutrition and wellness or careers in nutrition and food science:
- dietary consultant
- private dietary coach
- weight loss counselor
Careers in Nutrition and Dietetics
The United States and the world have finally begun to recognize the dangers of poor eating habits and the lifelong negative impact that poor eating habits cause. Fitness and health have become front-and-center issues. As a result, there is a surge in the demand for those who wish to follow a career in nutrition and dietetics.
The 21st century has brought about renewed interest in a career in nutrition and dietetics. Many careers in nutrition and health are available in the public and private sectors as policy setters and nutritional plan developers.
These bachelor’s in Nutrition jobs include:
- Chief dietitians
- Clinical dietitians
- Nutrition Educators
- Pharmaceutical Representatives
- Public health nutritionists
Careers in Nutrition and Health
For graduates who wish to focus their career on the relationship between nutrition, health, and exercise, consider these career options in the following situations:
- Advocacy healthcare groups
- Education communities
- Fitness facilities
- Government
- Health food stores and organizations
- Public relations
- Research facilities
Entry-level nutrition professionals with a bachelor of science in nutrition may find themselves working in the food industry, in a nutrition education program, or other health professions. You may also wish to go on to graduate study and earn a master’s degree.
Nutrition Science Jobs
Nutritional science jobs focus on how nutrition functions at a molecular or cellular level. This area of study dovetails with careers in nutrition and health that studies how to prevent disease and stress while optimizing one’s health. bachelor’s in nutrition jobs would include the following scenarios:
- Academia
- Consulting
- Food processing
- Governmental agencies
- Pharmaceutical industry
- Private health-related communities
- Research and development
Finally, it is noted that many students who graduate with a bachelor’s in nutrition further their studies in the fields of dentistry, medicine, optometry, and osteopathy, among other medically-related fields.
Nutritionist Salary: How Much Does a Nutritionist Make?
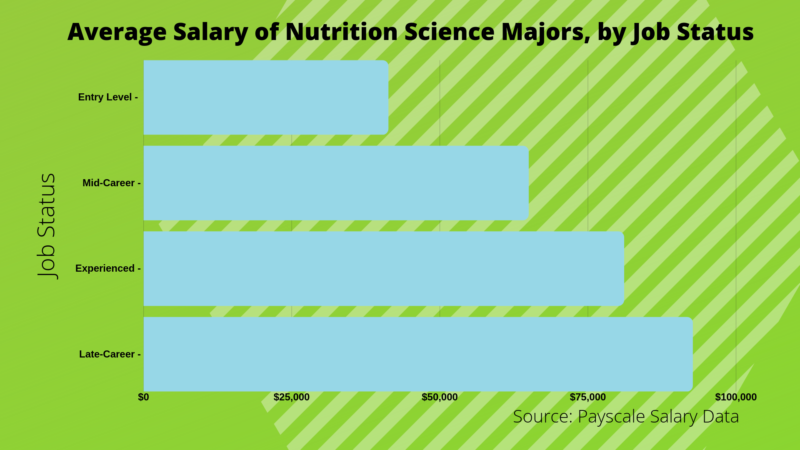
How much does a nutritionist make? A nutritionist salary varies depending on one’s level of education and chosen specialty. One can expect a dietitian salary to fall in line with the federal government’s Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). According to the BLS, a nutritionist or dietitian salary for 2017 hovered near the $60,000 mark.
A clinical dietetics salary per hour for 2017 was $28.56. Additionally, one can expect for the most part similar compensation for a nutrition science salary (a career that overlaps frequently with clinical dietetics) and other levels of nutrition science degree salary expectations.
The projected growth for the nutrition industry is anticipated to exceed the average growth of all occupations for the time period of 2016 — 2026. As a result, a bachelor’s in nutrition salary should rise strictly based on a growing demand. This should also happen for a dietetics degree salary, a clinical dietetics salary, a nutrition science salary, or a nutritionist salary.
Many nutritional program graduates are self-employed. The BLS notes that about eleven percent of nutritional degree graduates operate as self-employed consultants with yearly compensation that matches a clinical dietetics salary, a nutrition careers salary, or a nutrition science degree salary.
So how much does a nutritionist make? It varies depending on one’s education and specialization. Working for the government of a nonprofit may have its limits, but independent consulting, personal clients, and other more entrepreneurial efforts may mean paydays much higher than the average nutritionist salary or dietitian salary. So go ahead — head to Hollywood, hang out at Whole Foods, and find a star who needs nutritional advice.
Professional Organizations in Nutrition and Dietetics
The nutrition industry is regulated by several accredited agencies that provide licensing criteria and oversight, and continuing education courses to maintain one’s Registered Dietitian license. For students who are new to the following organizations, it is noted that membership in one of these professional nutrition organizations is a great technique for understanding the current job market an effective way to network with colleagues from across the country.
These professional organizations include:
- The Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics
- The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition
- The American Society for Nutrition
- The American College of Nutrition
- The Center for Nutrition Policy and Promotion
- The Society for Nutrition Education and Behavior
The Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics is considered the largest food and nutritional organization in the world. It was established in 1917 by a dedicated group of women during World War One. Today the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics membership exceeds 100,000.
The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition (AJCN) is the most highly regarded peer-reviewed publication.
The American Society for Nutrition focuses on nutritional research and offers professional archived research studies to enhance the industry.
The American College of Nutrition encourages the advancement of nutritional science.
The Society for Nutrition Education and Behavior(SNEB) is an organization dedicated to nutritional educators across the globe.
The Center for Nutrition Policy and Promotion (CNPP)is an agency within the U.S. Department of Agriculture. Its mission is to set forth healthy guidelines to help the population maintain a healthy lifestyle.
