Key Information:
- A degree in forensic science can lead to various roles in law enforcement, crime lab analysis, and legal settings.
- The study combines multiple disciplines including chemistry, biology, psychology, and law.
- Forensic science programs often require a deep understanding of scientific and investigative techniques.
Forensic science is one of the fastest-growing occupational fields, as developments in technology and criminology have made criminal investigations highly technical and scientific. The era of the “gut feeling” is long over – crimes are solved with science today, and thanks to shows like CSI, true-crime documentaries, and investigation podcasts, everyone wants to be a forensic scientist, and a forensic science degree is the place to start.
The study of forensic science uses interdisciplinary techniques and specialized protocols to appropriately gather and scrutinize data in support (or refute) of potential accusations, which are most often decided in a courtroom or related legal setting. It’s an education that is at once broad and highly specialized, and students are turning to criminal forensics in droves.
Related:
- Best Forensic Science Degree Programs
- Best Online Forensic Science Degree Programs
- Fastest Online Forensic Science Degree Programs
- Most Affordable Online Forensic Science Degree Programs
Do you find yourself wondering:
- What can I do with a Forensic Science degree?
- Is Forensic Science a good major for my career goals?
- Is Forensic Science hard?
- Is Forensic Science a good major?
- What can I do with a Forensic Psychology degree?
First, it is worth noting that with a degree in forensic science, you will be able to personally contribute to making the world a safer place by working with members of law enforcement using cutting edge investigative techniques.
A Clear Forensic Science Definition
The field of Forensic Science began in Europe, during the latter part of the 19th Century. The use of the art of fingerprinting exploded when law enforcement professionals realized the ease in which scientific data facilitated the solving of criminal investigations
A forensic science definition finds its roots in Latin. Forensis, which means a public forum or public discussion that, is argumentative and rhetorical in nature. The word forensic has been used as a substitute for the term “court-related” in the past. Recently, though, the concept of forensics has evolved to include a strong science correlation.
Forensic Science encompasses many fields of study that combine to define how scientific knowledge and technology are used in the fields of crime and law. Those interested can opt for collecting and cataloging evidentiary data, while other students prefer positions in crime labs analyzing scientific data.
Forensic Science is an interdisciplinary approach that draws from the best practices from the fields of:
- Anthropology
- Biology
- Chemistry
- Engineering
- Genetics
- Medicine
- Pathology
- Pathology
- Psychiatry
- Toxicology
So let’s answer the questions noted above.
What can I do with a Forensic Science degree? A Forensic Science degree opens up a wide variety of potential occupations as the profession using techniques from the fields of chemistry, biology, and computer science, among many others.
Is Forensic Science a good major for my career goals? If one’s career objectives relate to the fields of law enforcement, technological applications, or crime, then a major in Forensic Science is the right fit.
Is Forensic Science hard? The concept of difficulty is relative. That is, it is impractical to determine ‘how hard’ the coursework will be without knowing the interested student. Students with inclinations toward, science, law, and technology find a Forensic Science degree valuable.
Is Forensic Science a good major? For degree seekers who wish to work in the private or public safety sector, Forensic Science is a great major.
What can I do with a Forensic Psychology degree? Forensic Psychologists find exciting careers as Victim Advocates, Probation Officers, Court Liaisons, or Law Enforcement professionals.
School and Program Accreditation for Forensic Science
Accreditation is the process by which institutions of higher learning are assessed based upon a standardized peer review. The United States’ began accrediting schools and programs near the turn of the 20th Century.
Accreditation is performed by a neutral, ‘3rd-party’ agency. Accreditation can cover general divisions, departments, and schools, or specific degree programs. The process of accreditation is conducted by determining if a school or program meets the standards set forth by oversight agencies and local law. From a student’s perspective, the accreditation process helps ensure the degree program meets the industry criteria, and thus, the student receives the education promised.
In the United States, accreditation denotes that the institution that a student is planning to attend is routinely assessed by an independent agency regarding the quality and standards of the education it offers. There are two types of accreditation: the first type is institutional, which refers to the entire institution of higher learning. The second accreditation is program-based and directly related to individual programs of study within a school.
Regional vs. National Accreditation
Regional accreditation differs from national accreditation. The main difference between the two types of accreditation is that regionally accredited credit hours are more widely accepted and thus, more easily transferable.
A regionally accredited college or university is typically a school that is either academically oriented, non-profit, and/or a state-owned institution. A regionally accredited institution reluctantly accepts transfer credits from a nationally accredited institution. The fundamental reason is due to the fact that a nationally accredited school has not met the more stringent criteria of regional accreditation.
Regional accrediting agencies oversee a particular geographic region of the United States. Some of these agencies provide oversight to larger regional zones. Regional accreditation agencies accredit postsecondary institutions as well as primary and secondary schools.
Nationally accredited schools are typically defined as for-profit schools providing degrees and certificates for those students interested in a vocational career, religious education or technical programs. Nationally accredited schools generally accept earned semester credits from other nationally accredited schools and regionally accredited schools.
Program Accreditation
The Forensic Science Education Programs Accreditation Commission (FEPAC)is tasked with the responsibility of maintaining and enhancing the integrity of the education for forensic science. This is accomplished by routine formal assessments by a forensic education oversight agency.
FEPAC’s accreditation applies to regionally accredited universities and schools. FEPAC’s mission is set forth rigorous standards and agreed-upon standards that define a high-quality forensic science program and to manage an accreditation process that identifies notable programs for students seeking a baccalaureate degree and/or a master level degree.
Types of Forensic Science Degrees
The sheer number of Forensic Science career possibilities is impressive. This is due to the fact that forensic scientists who hold a computer forensics degree have been trained as experts in a cross-disciplinary field that partners with the techniques that relate to law, science, psychology, technology, chemistry, and biology, among others. The field of forensic science offers career opportunities that require tremendous amounts of numerical analysis. The same field of study also offers cutting-edge careers that interpret data and evidence in an effort to come to a truthful conclusion. And for the psychologically minded student, check out the available forensic psychology online courses.
Finding the Right Forensic Science Major Offered by a Forensic Science University
Are you considering applying to one of the many quality Forensic Psychology schools or a program offered by a Forensic Science University? Or maybe you are interested in studying from a Crime Scene Investigator school instead? Do crime Scene Investigation colleges offer specialty programs that include advanced studies in a for a Computer Forensic Degree program, a forensic Chemistry degree, or a Forensic Psychology Degree program. Have you recently googled the phrases ‘Forensic Science degree near me’ or ‘Where to Study Forensic Science’?
If so, your search for a program related to forensic science bachelor degree programs from crime scene investigator colleges has just begun. And the good news is that these forensic science bachelor degree programs are easily accessible from the best universities for forensic science in the world. There are numerous crime scene investigator schools from which to select a specialty and the choice remains yours, and yours alone.
Traditional ‘brick and mortar’ schools offer face-to-face instruction for students vying for a Bachelors in Forensic Science degree. A Forensic Science major has the option to select from numerous areas and concentrations that include a Forensic Chemistry degree, a Computer Forensics degree, a Crime Scene investigation degree, or a Digital Forensics degree.
Crime Scene Investigation: Definition – A crime scene investigation degree prepares students to work in the field as crime scene investigators. In addition to the basics of forensics, education for a crime scene investigator requirements include a strong understanding of law (so investigations are done according to regulation) and of the criminal justice system.
Digital/Computer Forensics: Definition – A digital forensics degree gives students a strong grounding in computer science, but especially in areas like cybersecurity. Digital forensics degree requirements would include highly specialized training in data analysis, national and international law, and areas like finance and money laundering, since much digital forensics is about combating white-collar crime.
Forensic Chemistry: Definition – A Forensic Chemistry degree program requires the basics of any chemistry degree, but with special focus on the elements of chemistry that relate most closely to criminal justice. All sorts of chemical knowledge can help solve crimes, from poisons and gunpowder to unexpected compounds that can indicate cause of death or criminal cover-ups.
Forensic Psychology: Definition – A Forensic Psychology online degree offers an online forensic psychology degree that delves into the many facets of human nature and behavior. Coursework in Forensic Psychology schools focuses on the ways in which it impacts the psychology definition and crime scene procedures. Colleges that offer forensic science majors in psychology very often provide forensic science online courses free; should a student have no need for college credits. Online Forensic Psychology degrees open career opportunities for those interested in the world of psychology, law, and crime.
Crime scene investigator requirements and Forensic Science degree requirements are set by the schools that offer the digital forensics degree; whether on-campus or online counterpart.

Online Forensic Science Courses & Bachelors in Forensic Science Degree Programs
For students who require a more flexible approach to crime scene investigator training, there are many qualified, accredited online forensic science bachelor degree programs to choose from. There are Forensic Psychology online courses or a Crime Scene Investigation degree that is available by some offered by some of the best universities for forensic science in the world.
Most crime scene investigator colleges that offer forensic science majors have developed online forensic science courses and programs to provide students with the flexibility and convenience needed to accommodate busy professionals. So, it is likely that students, who wish to study for a forensic science degree online, will easily meet their objective of finding the right forensic psychology degree (or an online forensic science certificate) by a quick internet search. Within minutes students will be able to identify online forensic science bachelor degrees that meet their requirements.
A forensic science major that has earned their forensic science degree online-from a forensic science university — has the option to select from several specialty disciplines. Remember to consider the forensic science degree requirements and the crime scene investigator requirements when considering crime scene investigator colleges or crime scene investigator training programs.
Earning a Forensic Science Bachelor Degree Online
A forensic scientist has the option of studying in a brick and mortar classroom or by studying on a flexible distance-learning platform. While many students choose the more traditional path to earn their forensic science bachelor degree (i.e. on-campus), increasing amounts of student now choose among the many and varied distance learning degrees.
Upon completing online forensic psychology degrees, students have gained the knowledge required to understand a digital forensics definition, a crime scene investigator definition, and the overall computer science definition.
Whether you are vying to delve into the complexities of a computer forensics definition, searching for the perfect crime scene investigator educational opportunity or simply want to begin a forensic psychology online degree, you can be certain there will be an online forensic science bachelor degree that sets you on a path to reach for your dream job.
Certifications and Licenses for Forensic Science Careers
To move forward towards a successful career in computer forensics, students and professionals need to recognize that employers prefer to hire forensic science majors who hold a computer forensics certification or a digital forensics certification.
These certifications speak to a potential employee’s skills and professionalism. Holding a professional certification ensures an employee’s education and experience are up-to-date regarding cutting-edge technology and emerging digital and cyber threats. Consider earning one of the many forensic science certifications available in the industry as noted below.
ISC2: The International Information System Security Certification Consortium (ISC) is a non-profit association dedicated to the training of and the provisions of digital forensics certifications as well as computer forensics certifications. Most recognize ISC as the preeminent, influential IT security organization of professionals in the cybersecurity industry.
The need for an independent certification watchdog arose in the 1980s when industry experts recognized cyber security’s incredible growth and mounting impact on businesses and governmental entities. Between the 1900s and today, several certifications were borne from the idea. Note, several certifications have been renamed and/or upgraded.
- Certified Authorization Professional (CAP)
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP)*
- Certified Secure Software Lifecycle Professional (CCSLP)
- Healthcare Information Security and Privacy Practitioner (HCISP)
- Systems Security Certified Practitioner (SSCP)
* CISSP certification offers several subspecialties that include the Information Systems Security Management Professional (ISSMP), the Information Systems Security Architecture Professional (ISSAP), or the Information Systems Security Engineering Professional (ISSEP)
Each and every ISC Certification holder must complete a pre-determined set of continuing education annually, to maintain active certification. There are a number of ways to earn the required certification credits. This can be accomplished by attending IT events, contributing industry-related narratives to professional magazines or by reviewing books and other forensic science materials.
Additionally, ISC Offers an Associate of ISC Designation, which benefits those cybersecurity professionals who are currently on a path to earn their certification but do not have enough experience to obtain a certificate yet. An associates degree is a great way to gain experience and industry skills while working toward the certification of their choice.
Ethical Requirements
Professionals who hold a professional certification issued by ISC must adhere to a code of ethics. Failure to do so will result in an ethics panel review by one’s peers. The conclusion of the peer review could potentially lead to the revocation of a previously issued ISC certification.
It is noted that one of the original certifications — (CCFP) — issued by the industry is no longer available. Professionals can now choose from the varying certificate options within the computer forensics certification or the digital forensics certification.
Careers in Forensic Sciences: What Can You Do with a Degree in Forensic Science?
Now that you have your degree, what can you do with a forensic science degree? Forensic science degree jobs in most sectors of the economy. Crime Scene investigator jobs are in high demand from both the public and private segments across the country. They can be found in rural, suburban and urban settings.
A Forensic Science technician will find rewarding careers as a computer forensics analyst, a crime scene technician or, a computer forensics investigator. Within the healthcare sector, a forensic science technician has the opportunity to select from various forensic psychology careers, computer forensics jobs, crime scene technician jobs, and forensic psychology jobs.
Crime scene investigation jobs offer employment in the fields of law and police work. A crime scene technician will also find gainful employment by searching within available forensic chemistry jobs posts and determining which forensic chemist job description best fits their career objectives.
Digital forensic jobs, according to the American Academy of Forensic Sciences, are divided into a variety of forensic science jobs.
What Jobs Can I Get with a Forensic Science Degree?
What jobs can you get with a forensic science degree? The most popular crime scene investigation jobs are shown below:
Crime Scene Investigator — Crime scene investigator jobs or crime scene technician jobs are what we typically think of as forensics – gathering evidence, taking photographs, creating models, establishing timelines, and other on-the-scene investigation.
Digital/Computer Forensics — Digital forensic jobs are found in the many levels of government and in the business sector. Their specialty is used to support criminal investigations by analyzing computer systems, searching for the identity of hackers, and solving crimes involving technology. They frequently work in white-collar crime investigations.
Forensic Chemistry — Forensic chemistry jobs are available in a medical examiner’s office, crime labs, and/or police departments. Forensic chemists use their knowledge of chemistry to analyze everything from gunpowder residue to poisons and drugs.
Forensic Psychology — Forensic psychology careers apply the principles of forensic science with psychological theories and techniques. Forensic psychologist may use their expertise to create a psychological model of a suspect, determine motives, and understand the mindset of a suspect when they committed a crime. Forensic psychology jobs are also available prepping victims and witnesses to testify in court.
Your career path can go even farther with a master’s degree. Further job opportunities and career options include:
- Forensic accountant
- Forensic investigators
- Forensic pathologist
- Forensic engineers
- Forensic anthropologist
- Forensic nurse
In graduate programs, you will learn more about how to trace evidence, ballistics, autopsies, forensic toxicology, DNA analysis, criminalistics, and other scientific methods of working with physical evidence. A specialization like molecular biology or natural sciences can expand your options even more.
Salary Expectations in Forensic Science
The field of forensic science is an ultra-fast-growing industry. In fact, according to the federal government’s Bureau of Labor Statistics, it is estimated that the growth of the forensic science industry (and thus, the number of crime science investigators needed) will outpace the average rate of all industries combined.
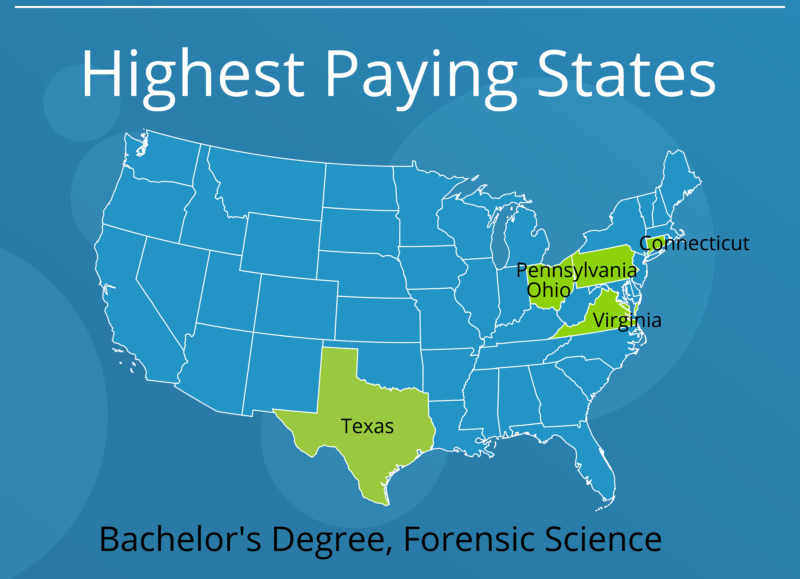
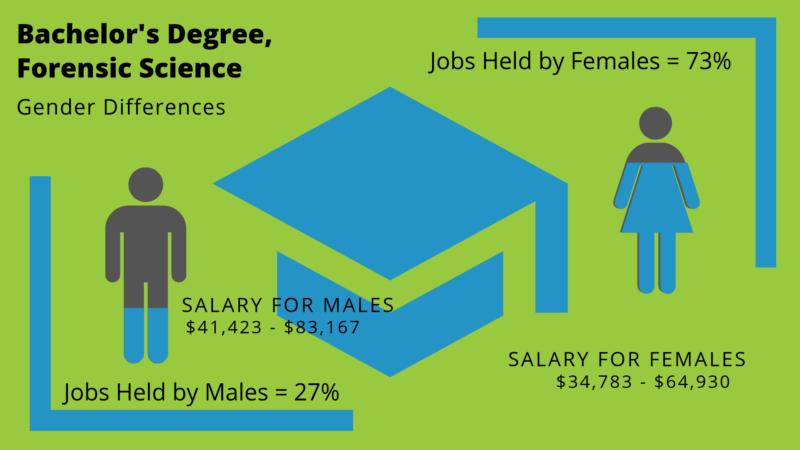
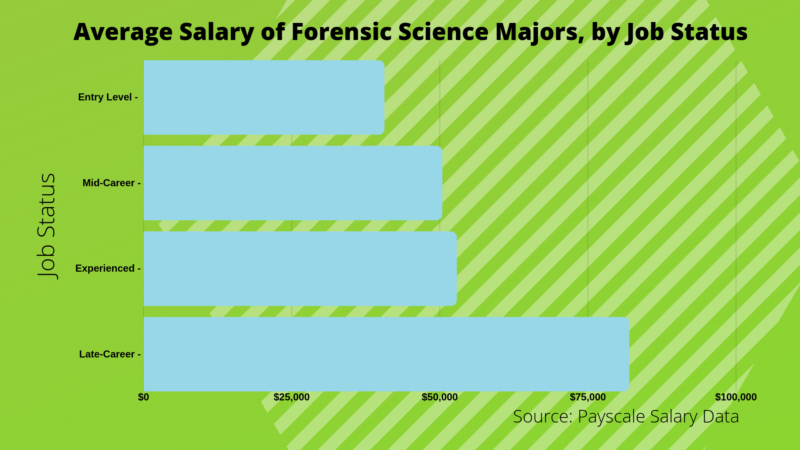
A forensic science degree salary average for 2017 was $57,850, or $27.81 per hour. However, that doesn’t take into account the diversity and variety of jobs in forensic science. Salaries can vary greatly. According to Payscale, average forensic science jobs pay:
Crime Scene Investigator Salary: Crime Scene Investigators make an average of $45,000 per year.
Digital/Computer Forensics Salary: The average Forensic Computer Analyst makes around $71,000 annually.
Forensic Chemist Salary: A Forensic Chemist will make around $55,000 on average.
Forensic Psychology Salary: Forensic Psychologists can expect to make something on the order of $64,000 a year.
Of course, a crime scene investigation salary increases as a forensic technician’s experience grows, or, a more advanced degree.
The crime scene investigator salary requires a technician to work independently in the field, the office or a crime science laboratory. Remember, though, that a computer forensics salary will be similar, but never will be the same when compared with a digital forensics salary or a forensic chemist salary, for that matter. Each crime scene job has its own required set of skills.
The majority of crime scene opportunities offer employees benefits that include medical and dental insurance, paid time off (PTO), disability insurance, paid continuing education, and various forms of retirement planning.
Professional Organizations in Forensic Science and Criminal Justice
Professional organizations in forensics, like associations in other occupations and industries, serve many purposes. First, and foremost, the members of an organization give back to the forensic science community; they make a difference. Organizations work towards a common objective with many members. The combined effort of many organizations creates enough influence to effectuate change.
A professional organization offers professional development courses and certificate-granting classes, which are required as set forth by state standards. They also organize job market platforms for members in search of a job. The field of forensic science has several professional organizations, each serving a specific purpose.
The American Academy of Forensic Sciences: The American Academy of Forensic Sciences’ (AAFS) purpose is to provide effective leadership while contributing towards the advancement of forensic science and how it applies to the law. The AAFS stands for professionalism, education, and research through a collaborative effort by forensic scientists. Their industry benchmarks set the standard regarding competency, ethics, and integrity.
The Chartered Society of Forensic Sciences: The Chartered Society of Forensic Sciences (The Society or CSFS) is a worldwide professional organization with forensic scientists members representing more than 55 countries.
The Consortium of Forensic Science Organizations (CFSO) consists of six member organizations in the field of forensic science. The consortium was established in 2000 and together, it represents more than 20,000 forensic scientists in the nation. Member organizations include:
- American Academy of Forensic Sciences
- American Academy of Psychiatry & Law
- American Society of Crime Lab Directors
- International Association for Identification
- National Association of Medical Examiners
- Society of Forensic Toxicologists
The Consortium of Forensic Science Organizations was created to speak with a unified voice of forensic science professionals in regard to the modification of national public policy, and to advocate for the governmental funding of crime labs in the public sector, among other issues.
The National Association of Medical Examiners: The National Association of Medical Examiners (NAME) is a nonprofit organization that was established over a hundred years ago. This professional organization manages the United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE), a forensic science professional license process and database.
The Society of Forensic Toxicologists: Members adhere to the guiding principles set forth by the Society of Forensic Toxicologists (SOFT). These guiding doctrines include Professionalism, Clear Communications, Proficiency, and Ethical Compliance.
