Key Information:
- Education degrees offer various specialization options like early childhood, elementary, secondary, and special education, catering to a wide range of teaching careers.
- Dual certification and specialization in high-demand areas like ESL or special education can enhance job prospects, flexibility in teaching assignments, and lead to higher salaries and professional growth opportunities.
- There are two main types of education degrees: Bachelor of Arts (BA) focusing on liberal arts and Bachelor of Science (BS) focusing on technical subjects. The choice depends on the prospective teacher’s career goals and interests.
Why become a teacher? Do you have a passion for teaching? Do you want a rewarding and fulfilling job (one with benefits and tenure, preferably)? Put the two together, and it becomes apparent that one of the best college degrees for jobs is a Bachelor’s in Education degree.
But why become a teacher? There are a number of reasons. The best college degrees for jobs are the ones that have the most job available, and there’s not a state or county in the country that doesn’t need more teachers. On top of job availability, teachers can count on benefits like retirement, paid sick leave, health insurance, and professional development time. And in the end, many people become teachers because making a difference in people’s lives is rewarding in itself. So with all that, what can you do with a bachelor’s in education?
Related Rankings:
- Best Education Degree Programs
- Best Online Education Degree Programs
- Best Affordable Online Education Degree Programs
Education for Educators
Before completely committing to an education program, it is important to ascertain the accreditation status of the program or school. Receiving an unaccredited degree is a waste of both time and money. Virtually no employer — especially not in a public school, which has official standards of accountability — will take an unaccredited education degree seriously. Because of that, it is good to know what accreditation means and how to look for accredited education degree programs. Searching for programs that have gone through the accreditation process to meet CAEP standards, NCATE accreditation (the National Council for Accreditation of Teacher Education), and other benchmarks is your first step.
Why Accreditation Is Important for an Education Degree Program
The accreditation process means an officially recognized, independent accrediting agency evaluated a school or degree program. That evaluation ascertains if the program meets or exceeds specific quality standards. These agencies set the standards and make sure the institution adheres to them. If an institution does not meet those standards or fails to meet them at any time, it can lose that accredited status.
Different types of degrees must meet different standards. Because of that, many different accrediting agencies exist. In addition, an agency’s accreditation process can give accreditation to an institution in full, or to only a single program. Broadly, there are two types of accreditation: regional and national.
What is Regional Accreditation?
Regional accreditation is the most recognized form of accreditation for universities and institutions. The six Department of Education-recognized regional accreditation agencies assign accreditation to higher education institutions. Credits from regionally accredited degree programs have a broad acceptance around the country.
Accreditation from the regional agencies usually falls under the term “institutional accreditation.” The term implies that the entire institution received accreditation and all of its courses and programs serve the overall governing standards.
The six regional accreditation agencies include:
- Middle States Commission on Higher Education (MSA)
- New England Association of Schools and Colleges (NEASC)
- North Central Association of Colleges and Schools (NCA)
- Northwest Commission on Colleges and Universities (NAC)
- Southern Association of Colleges and Schools (SACS)
- Western Association of Schools and Colleges (WASC)
Regional accreditation represents the most recognized type of university accreditation. The credits earned in a regionally accredited college have a higher likelihood of being accepted for credit transfers.
What is National Accreditation?
Strange as it may seem, regional accreditation is the larger accreditation, extending to a whole college or university, while national boards usually accredit specific degree programs. National accreditation typically means the program has a specific educational focus. National accreditation also falls under the terms program, programmatic, or specialized accreditation. The names denote that this type of accreditation typically applies to particular types of programs.
Vocational, trade, technical, and other programs will usually receive national accreditation for their focus on standards related to a specific industry or job type. Because of the specialized nature of these programs, they are not usually subject to the standards set by regional accreditation agencies. Rather, specialized national accreditations usually fall under regional accreditations.
Accrediting agencies for national accreditation can vary widely. Some industries or job types have their own accrediting agencies. For example, the American Bar Association evaluates and gives accreditation to law programs and degrees specifically.
Accreditation for Education Programs
For education degrees specifically, both regional and national accreditation exists. The most well-known and respected accreditation agency for teaching programs and degrees is the Council for the Accreditation of Educator Preparation (CAEP). The CAEP sets the standards and certifies nearly all teaching programs in the country.
Note: The CAEP is a merger of two of the largest US DOE recognized teaching accrediting agencies. That means it is possible to still find programs listed with the former agency names as accreditors. Those two agencies are:
- The National Council for Accreditation of Teacher Education (NCATE)
- The Teacher Education Accreditation Council (TEAC)
So, seeing TEAC or NCATE accreditation is the same as seeing CAEP accredited online schools and other institutions. On the other hand, NCATE accreditation still means the program or institution adheres to the current CAEP standards.
Those seeking a bachelor’s in education degree, or those specifically seeking a program that deals with teaching can both look for CAEP accreditation and adherence to CAEP standards. This will apply whether the applicant is looking for an online course, a traditional university, or another teaching-related program. For teaching positions and opportunities, a CAEP accredited degree has a nearly universal acceptance.
Not all unaccredited education programs are inherently bad. Some may offer just what an applicant needs. Nevertheless, choosing an accredited program is always the safer choice to make.
What are the Different Types of Education Degrees
Education degree types vary, but they all can help someone reach their goals. A bachelor’s degree in education exists in two main varieties:
- Bachelor of Arts (BA) in education
- Bachelor of Science (BS) in education
Regardless of which of the education degree types you choose, a bachelor’s degree in education will give applicants the tools they need to manage a classroom and delve into the psychology of those they intend to teach. The main difference between the education degree types, the BS or BA, is the coursework focus.
The BA usually includes more liberal arts instruction such as courses in humanities, social sciences, art, and communication. The BS will have more focus on technical fields, such as math, science, and physics. Choosing which type of bachelor’s degree to pursue will require an applicant to have some idea about where they want their teaching career to go.
In addition, a bachelor’s degree in education will typically allow an applicant to pursue a specialty. The minor subject that accompanies the education major will help an applicant learn what they need to enter a specific field.
Education Specialization Options
Choosing a specialization is important. Depending on what the applicant wants, there are numerous options available. Some specializations can include:
Early childhood education – For those who want to teach children between two and five years of age.
Elementary education – For applicants who want to teach students between kindergarten and middle school. The elementary education degree is one of the most sought after. An elementary teacher degree has a lot of flexibility depending on where the applicant wants to teach.
Secondary education – This specialty is for applicants who want to teach high school students.
Special education – Special education encompasses a number of different focuses. An applicant would choose a special education path if they want to teach children with a specific aptitude or disability. For example, teaching an autistic child would require the applicant to have a bachelor’s degree with that particular specialty.
To give an example, consider an applicant who wants to teach English as a second language. That applicant would pursue a BA with a special education minor in Spanish.
The applicant will then have the education they need to teach ESL at public and private institutions. Also, and ESL specialty is actually a highly sought after one, so someone with that education will have a larger pick of teaching jobs.
Other specializations include:
- adult education
- curriculum design and curriculum development
- instructional coordinator
Other roles, like education administration, education policy, instructional designer, educational consultant, and more, might require a master’s degree.
There are also non-education careers that can benefit from an education degree, such as career counselor, school counselor, corporate trainer, recruiter, guidance counselor, and more. Education professionals have developed strong problem-solving, management skills, leadership skills, and communication skills. After all, there’s much more to childcare than making lesson plans.
No education degrees list is complete since teaching is something that can become incorporated into literally any industry. That is another reason why applicants should have a good idea on where they want to take their teaching career beforehand. The specialty route means applicants do not need multiple education degrees in order to pursue a particular career path.
Get Your Teaching Degree Online
You can definitely get your teaching degree online — in many cases, you can do it without ever having to attend a class on campus. In fact, for many people, accredited online teaching degree programs are an ideal situation, since they is much more convenient, and often cheaper, than a traditional on-campus program. Becoming a teacher online comes with the same considerations as obtaining a bachelors in education any other way.
When looking for a teaching degree online, applicants should make sure the offered coursework lines up with the specialty they need. Accredited online teaching degree programs are available in all kinds of specializations, including online early childhood education degrees, and online bachelors degree elementary education.
Getting a secondary education degree online or any other type still requires the due diligence of the applicant. Becoming a teacher online still means vetting the schools and programs to make sure you are dealing with accredited online teaching degree programs.
Can You Get Teaching Jobs Without Degree In Hand?
When you get your teaching degree online, it should help you get a teaching job, but there are a few possibilities to find teaching jobs without degree in hand. Many people have found work teaching without a bachelor degree education. However, most places have bachelor degree in education requirements and will not consider any applicants that do not have their degree.
Nevertheless, some people with experience or a lesser degree can sometimes find work teaching entry-level classes to foreign language students. In some cases, a school or other institution might consider someone with one type of degree for a different job if that school is short on people.
For example, having an elementary education degree might be enough for a school to offer a different type of placement. In almost all cases, it is better to have a bachelor degree education at least to be taken seriously.
Some teaching jobs may not require any degree, certification, or teaching credentials at all. In some places, a teacher’s assistant doesn’t need a degree.
It doesn’t hurt to check local schools and institutions for jobs that don’t require a degree. This can help many who want to work in the field or at a learning facility while they complete their bachelor’s degree online
What Types of Certifications and Licensing are Required for Teaching?
An education degree is not all someone needs to start teaching. Since teaching is a regulated field, people who to teach will also require licensing or certifications.
Many bachelor’s degree programs also include the necessary coursework and testing that allows an applicant to earn their education license or certification as part of the degree program — they have teaching certificate requirements built in. Joining a program specifically for a particular education license or certification is also possible.
Both education license and teaching certificate requirements vary by state, so applicants should look into the teaching certificate requirements for their particular state. Applicants should know that the terms “licensed” and “certified” can mean the same thing or different things depending on the state. Generally, the terms will mean someone has received the state’s approval to teach.
Teaching certificate requirements towards an education license will typically involve coursework and testing. In most cases, the teaching certificate requirements will also include:
- Completion of a bachelor’s program
- Transcripts
- Background check
- Entrance exams and tests
Nevertheless, sometimes a certified teacher may need to become licensed to teach in a specific field. The opposite is also true when a licensed teacher needs to pass teaching certificate requirements to pursue other teaching avenues. When pursuing licensing or certification, applicants must make sure they are pursuing the right kind of teaching authorization.
Since applicants can pursue licensing or certification outside of full degree programs, many states offer fast-track teaching certification programs. These types of programs can help someone obtain their education license quickly, which is ideal for those who already have a bachelor’s but need to get their authorization to teach. A fast-track teaching certification isn’t any less rigorous — it has the same teaching certificate requirements, just faster.
Alternative certification teaching is something that can help those who already have entered the teaching field but want to make a change. For example, moving to another state or having the desire to teach high school instead of elementary school can sometimes be accomplished by earning an alternative certification teaching job.
Many states also offer alternative certification teaching for professionals who have an advanced degree besides teaching and want to teach — say, for instance, an experienced businessperson who wants to teach business to local high schoolers. Like a fast-track teaching certification, alternative certification has high standards but helps states get teachers in the classrooms where they’re needed.
What Types of Education Major Jobs are Out There?
A tremendous amount of education careers exist. Jobs within education offer different types of teaching jobs that can suit anyone. An exhaustive list of careers in education field is not possible. Practically every position in any school becomes conceivable with an education degree.

What Kind of Jobs Can You Get With a Teaching Degree?
As mentioned, all public and private school teaching positions for students from pre‑k through high school are the focus of an education degree. These are the typical education major jobs. https://www.bls.gov/ooh/education-training-and-library/home.htm However, some of the best careers in education can also include:
- Technical education teachers
- Career training and advancement teachers
- Teachers of adult classes, such as GED and literacy
- Library technicians
- Youth counselors
- Teacher assistants
Each teaching degree comes with other career opportunities. For example, once an applicant meets the requirements for elementary teacher positions, they do not only have to teach elementary students in a public school or at any school. They can teach elementary students in private schools, or mentor individual students, or start their own teaching program for people who want a personal tutor for their children.
A quick search of any online education careers list, education career information sites, or job openings page will show and prove just how valuable an education degree really is. The best careers in education, including high-paying careers education degrees, are out there, especially since there are so many different careers in education to pursue.
Because of the possibilities, becoming a teacher online or through other means will always represent an excellent educational investment.
What Alternative Career Options Are Available for Teachers?
Are you wondering what to do with a teaching degree besides teach? Teaching is not only something that happens in the classroom. Some of the best careers in education aren’t in education. There are many companies that hire teachers. Training and educating people is what an education degree prepares applicants for.
Even if an applicant chooses to teach in the classroom, they can still find other works as well. Second careers for teachers can help them earn more money, specialize in a particular niche or industry, and generally make themselves more valuable to companies to hire teachers.
Some people may want to continue teaching, but feel they need to go on a different career path to do it. Great career changes for teachers start with their degree program. Applicants can figure out what to do with a teaching degree besides teach if they look around and are willing to pursue some of the opportunities.
Second Careers for Teachers
Teachers who change careers have quite a few options. Companies that hire teachers can range across all fields, not just industries related to education. Great career changes for teachers can include:
- Companies that develop educational tools
- Youth organizations
- Writers and writer assistants
- School administration
- Online tutoring and coaching
- Community education officer
- Businesses that need to develop training materials
Someone with an education degree and an open mind will likely find companies that hire teachers and careers in education other than teaching. Because of the flexibility of an education degree, applicants will always have the ability to go beyond classroom teaching. There’s no question what to do with a teaching degree besides teach — there is no shortage of second careers for teachers.
In some cases, an applicant may choose an education degree with the specific goal of entering a non-traditional or non-academic teaching career. An example of this is someone who works at a corporation who wants to advance to a senior training position. An education degree can help find positions with companies that hire teachers.
Applicants wondering what to do with a teaching degree besides teach should not assume an education degree is only good for teaching. Great career changes for teachers are everywhere. Choosing to go the education route can also represent an entrepreneurial move, with second careers for teachers looking like very good bets. .
Education Careers and Salaries
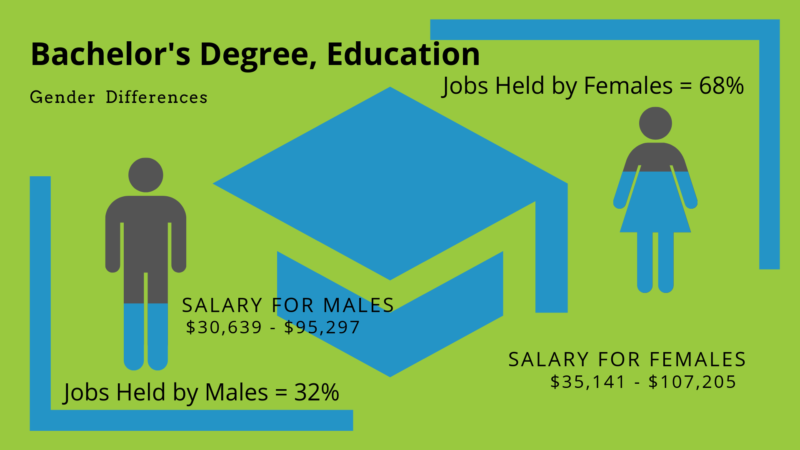
Teacher salaries vary widely depending on many factors. According to the Occupational Outlook Handbook, the median annual wage for education and training jobs was $48.7k in 2017.
Education careers and salaries do not always match up. For example, the median salary for an adult literacy teacher with a bachelor’s degree was at $52.1k, but that does not mean adult literacy teachers across the country are seeing that same number. Some will make more and some will make less.
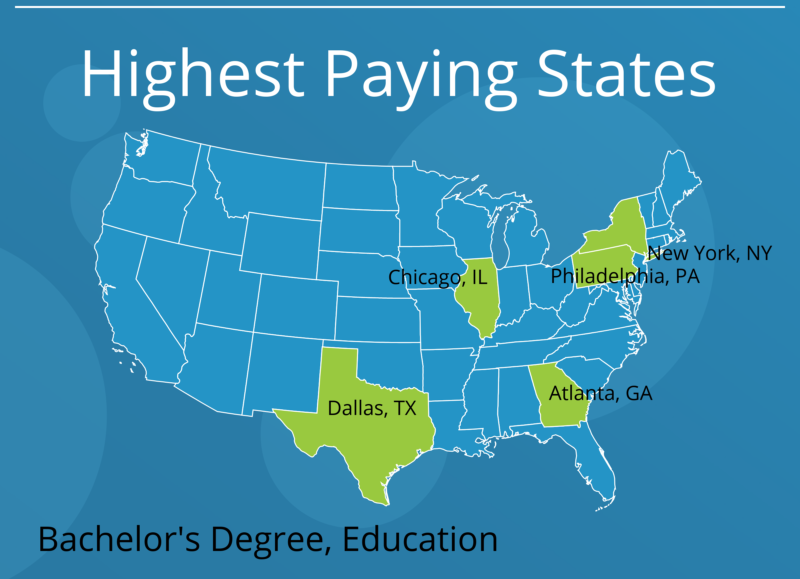
Applicants should not look at the median wage only. They should look to see salaries for specific states or regions. Do not just look at average high school teacher salary. Instead, drill down to find the high school teacher salary by state.
How Much Do Teachers Make an Hour?
A major question for potential teachers and even everyday people is “how much do teachers make an hour?” The question comes up often because, over the years, a lot has been said about teacher salaries in the news and other media.
As with most things, teacher salary per month, teacher salary per week, and teacher salary per hour can fluctuate greatly from place to place. In addition, asking how much do teachers make an hour negates the fact that there are many different types of teachers.
For applicants looking for the right information, the search for an hourly wage number should include the type of teacher and the state. High school teacher salary by state can differ widely, for instance. A better question, for example, is “how much do elementary teachers in South Dakota make per hour?”
Differences in Salaries for Teachers
Median salaries for teaching jobs can range from $25k to $60k. That translates to about $12/hour up to nearly $30/hour. Some teachers make even more depending on where they are at and whether the collective bargaining of their organizations or unions has helped to obtain more.
The average private school teacher salary will usually hit higher numbers than the teacher salary per hour at a public school. Equally, the elementary teacher salary is usually lower than a secondary school teacher’s salary.
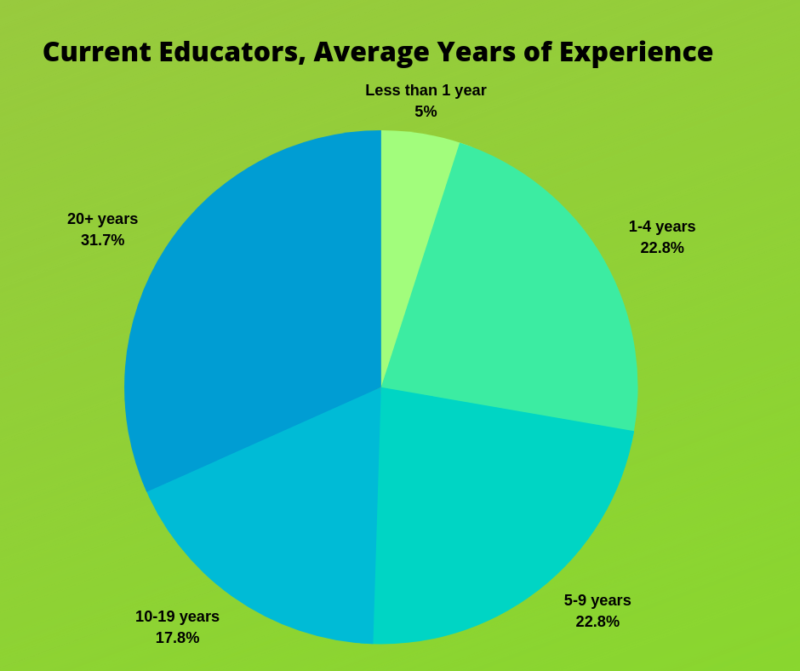
Yet, an elementary school teacher that tutors or teaches in a non-traditional venue may earn a far larger elementary teacher salary. In addition, tenure also matters. Entry-level salaries for a teacher are not the same as the salaries given to experienced teachers.
Professional Organizations for Teachers
Many professional organizations for teachers exist. Much like any trade, teaching comes with unions, professional groups, and clubs specifically for teaching professionals. Applicants should familiarize themselves with these groups and what they do.
Why is it Important for Teachers to Join Professional Organizations?
There are many reasons for teachers to join a professional organization, and no real reasons for them not to. Here are just a few reasons to why is it important for teachers to join professional organizations:
- Organizations provide resources
- Organizations help educators increase their knowledge
- Organizations provide invaluable networking opportunities
- Organizations often provide fellowships, scholarships, and grants
- Organizations look good on a teacher’s resume
The many professional organizations for teachers can sometimes make it hard to find the right one for an applicant’s needs. Some organizations even cater to specific types of educators. Some of the more popular, professional, and recognized professional organizations for teachers include:
American Association of School Administrators
American Federation of Teachers
Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development
Association of American Educators
Computer Using Educators
National Association for Bilingual Education
National Council of Teachers of English
National Education Association
National Science Teachers Association
Many more organizations exist beyond these; the University of New Mexico offers a comprehensive list. A good place to start with figuring out which organization is the right one is to look at the National Education Association. The NEA is the largest professional teaching organization in the country. Applicants do not have to join, but they can look at what the National Education Association offers to get a good idea of how important professional organizations for teachers really are.
These organizations help to develop and consistently improve both teaching and the lives of teachers. For example, the code of conduct for teachers typically arises out of professional teaching organizations. When issues affect the teaching field as a whole, these organizations tend to step up to make things right.
Also, many places have a local teacher organisation applicants can join and learn from. The downside to some organizations for newer educators is that many of the most reputable ones come at a cost. However, that cost is usually worth it.
But, until the applicant can join the ranks of one of the higher tier professional teaching organizations, they can look into education non-profit organizations or free membership professional organizations.
A bachelor’s degree in education can pay off in a big way, in terms of career satisfaction and return on investment. Just make sure you do your research and go about the process the right way.
